Boiler is a kind of heat exchange that converts chemical energy stored in coal, petroleum, combustible gas and biomass (wood, bagasse, platycodon, etc.) and waste heat in industrial production or other heat sources into water or steam at a certain temperature and pressure.
Boilers are widely used in various fields of the modern society and national economy. At present, more than 70% of China's electricity is obtained by using steam to drive turbine generator sets to generate electricity. Industrial and agricultural (such as textiles, chemicals, papermaking, machinery, agricultural products processing industries, etc.) Steam is also inseparable from the production process, and the heat energy required for heating, ventilation, air conditioning and domestic hot water supply also comes from high-temperature hot water or steam.
Therefore, the boiler has become an indispensable special important equipment in modern society's production and people's lives.
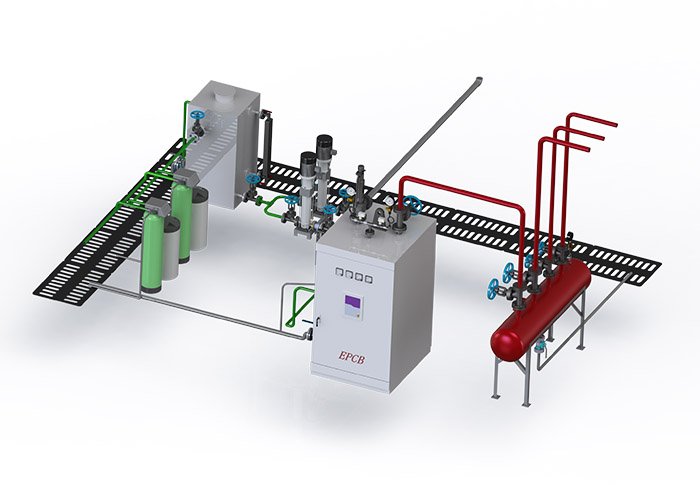
Boiler Composition
The boiler equipment is composed of two parts: the boiler body and auxiliary equipment.
1. Boiler body
The boiler body is composed of a combination of two parts: the "boiler" (the heating surface system that receives the heat of the high-temperature flue gas and transfers it to the working fluid) and the "furnace" (the combustion system that converts the chemical energy of the fuel into thermal energy).
"Boiler" refers to the various components that bear internal or external pressure and constitute a closed system, including the shell, the drum (the upper drum of the steam boiler is also called the steam drum), the downcomer, the header (header), and water cooling. Wall, slag tube, boiler tube bundle, steam-water separation device, steam temperature control device, sewage device, steam superheater, economizer, etc.
"Furnace" refers to the various components that constitute the fuel combustion site, including combustion equipment consisting of furnace (combustion chamber) and front coal scuttle, coal gate, grate (grate), slag removal plate distribution and air supply device.
2. Boiler auxiliary equipment
(1) Fuel supply system equipment
The function of fuel supply system equipment is to ensure the supply of fuel that meets the quality requirements required for the continuous operation of the boiler.
1) Fuel storage equipment includes coal yard, raw coal silo, pulverized coal silo, oil storage tank, working oil tank, etc.
2) Fuel transportation equipment includes belt conveyors, scraper conveyors, multi-bucket elevators, electric hoist hoisting coal tanks, single bucket elevators, coal feeders, powder feeders, bridge grab cranes, and coal pushers Engines, oil pumps, oil pipelines, gas pipelines, filters, pressure regulators, etc.
3) Fuel processing equipment includes crusher, coal mill, coarse powder separator, fine powder separator, powder exhaust fan, coal briquette, etc.
(2)supply and induced air equipment
The function of the air delivery and induced air equipment is to send the air needed for combustion to the furnace or to deliver the hot air desiccant to the coal grinding system, and to draw the combustion product-flue gas from the furnace to ensure the boiler burns normally. Air supply and induced air equipment include blower, induced draft fan, cold air duct, hot air duct, flue and chimney, etc.
(3) Steam and water system equipment
The steam and water system includes three major systems: steam, water supply, and sewage.
The function of the steam system is to send qualified steam to the user or the boiler's own steam. Steam system equipment includes steam pipes, accessories, sub-cylinders, etc.
The function of the water supply system is to send the treated water that meets the boiler water quality requirements to the boiler to ensure the normal operation of the boiler. Water supply equipment includes boiler feed water pump, water tank, water supply pipe, regenerating liquid pipe, water hardening, alkali removal, salt removal and degassing equipment, etc.
The function of the sewage system is to remove the sediment and salt impurities in the boiler water, so that the boiler water meets the boiler water quality standards. Decontamination system equipment includes sewage pipes, accessories, continuous blowdown expanders, regular blowdown expanders, blowdown cooling tanks, etc.
(4) Ash and slag removal equipment
The function of ash removal equipment is to continuously remove and transport the ash and slag of the boiler's combustion products to the ash and slag field. Ash and slag removal equipment includes Martin slag remover, impeller slag remover, screw slag remover, scraper slag remover, heavy chain slag remover, hydraulic ash removal system, ash tank, slag yard, slag bucket, bridge type Grab crane, ash pusher, etc.
(5) Flue gas purification system equipment
The flue gas purification system includes equipment for dust removal, desulfurization, and denitration of the flue gas. Their function is to remove the solid particles entrained in the boiler flue gas—fly ash, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide and other harmful substances, and improve Atmospheric Environment. Dust removal, desulfurization, and denitration equipment include gravity dust collectors, inertial force dust collectors, centrifugal dust collectors, water film dust collectors, bag filter dust collectors, electric dust collectors, sulfur dioxide absorption towers, denitrification devices, etc.
(6) Instrumentation and automatic control system equipment
The function of instrumentation and automatic control system equipment is to carry out automatic detection, program control, automatic protection and automatic adjustment of the running boiler. Instrumentation and automatic control system equipment include microcomputer, temperature, pressure, water level, flow, negative pressure and other instruments, flue gas oxygen meter, automatic regulating valve and control system.
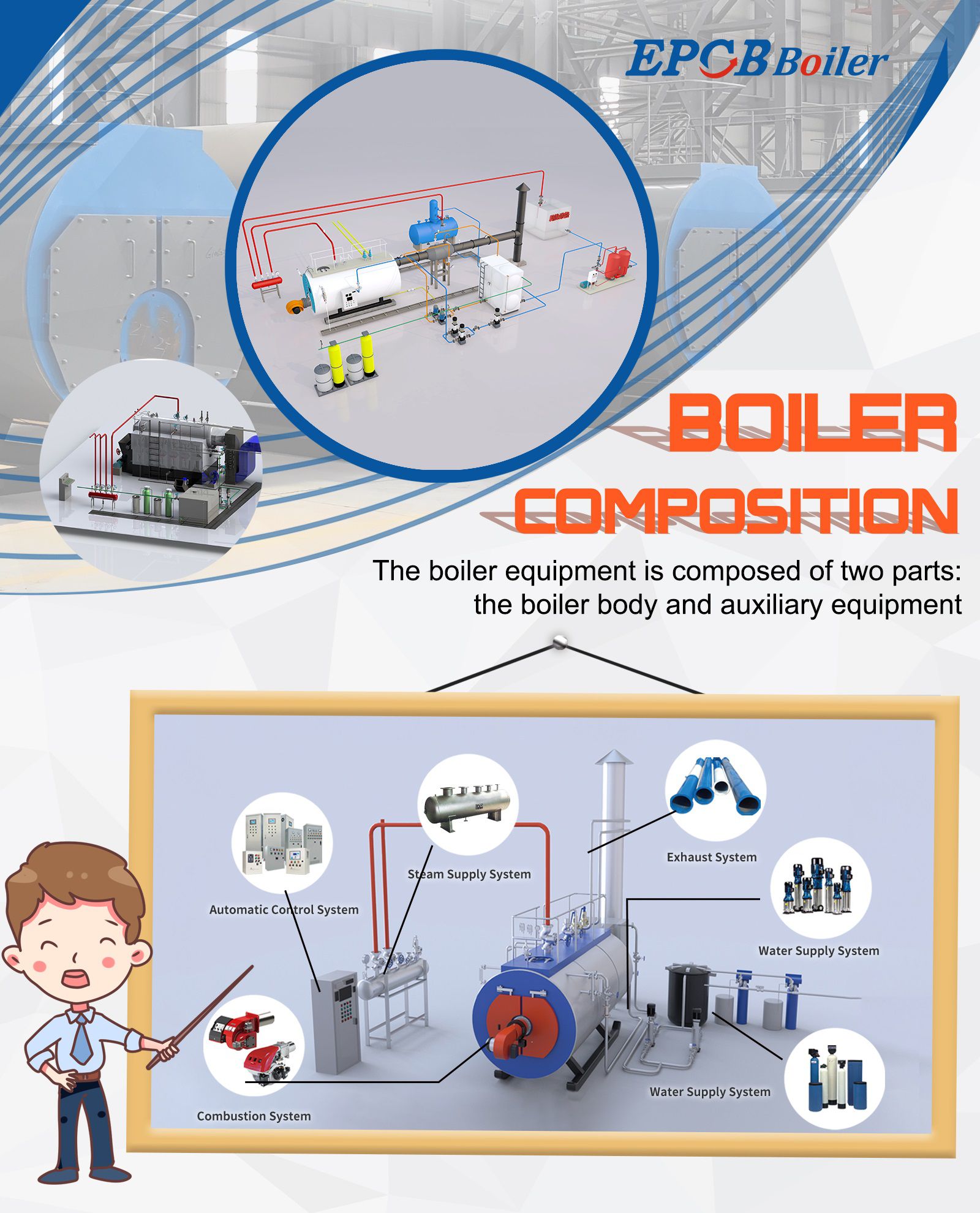
Boiler Classification
Boilers have a wide range of uses and types, and it is difficult to use a unified classification method to describe them. They are often classified from different angles.
1.Classified by purpose
(1) Industrial Boilers
Boilers used in industrial production, heating and ventilation, air conditioning projects and domestic hot water supply. Most of them are low-parameter, small-capacity boilers. The rated evaporation capacity of steam boilers is in the range of 0.1-65V/h, the rated thermal power of hot water boilers is in the range of 0.1-174.0MW, and the rated thermal power of atmospheric boilers is in the range of 0.05-2.8MW.
(2) Power Station Boilers
For power generation, it is a high-parameter, large-capacity boiler. Among the current standard parameters and capacity series of power station boilers in my country, the rated evaporation capacity of the largest-capacity boiler is 2008t/h, and its power generation is 600MW. The supercritical parameter steel guard has always been included in the standard.
(3) Marine boiler
Used as ship power, most of them are low-to-medium-parameter portable oil-fired boilers.
(4) Locomotive boiler
Most of them are low-parameter, small-capacity, portable coal-fired boilers used as engine power. There are very few applications at present.
2. Classified by working pressure
(1) Atmospheric pressure hot water boiler
In any case, the gage pressure at the boiler water level is zero.
(2) Low-pressure boilers
Boilers with rated outlet working fluid pressure (gauge pressure) p≦2.5 Mpa.
(3) Medium-pressure boiler
The rated outlet working fluid pressure of the boiler (the boiler with gauge pressure P=3.82 Mpa.
(4) High-pressure boiler
The rated outlet working fluid pressure of the boiler (the boiler with gauge pressure P=9.8 Mpa.
(5) Ultra-high pressure boiler
Boiler rated outlet working fluid pressure (gauge pressure) p=13 7MPa boiler.
(6) Subcritical boiler
Boiler rated outlet working fluid pressure (gauge pressure) p= 16.7MPa boiler.
(7) Supercritical and ultra-supercritical boilers
Boiler rated outlet working fluid pressure (gauge pressure), P>22. 13MPa boiler.
3. Classified by fuel or energy used
(1) Coal-fired boiler
Boilers that uses coal as fuel.
(2) Oil boiler
Boilers that use liquid fuels such as light diesel oil and heavy oil as fuel.
(3) Gas-fired boiler
Boilers that use gaseous fuels such as natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas, and artificial gas as fuel.
(4) Mixed fuel boiler
Boilers that use coal, oil, gas and other mixed fuels as fuel.
(5) Biomass energy boiler
Boilers that use biomass as fuel. Such as straw boilers, garbage incineration boilers, bagasse boilers, etc.
(6) Waste heat boiler
Boilers that use industrial waste heat and gas as the heating medium in metallurgy, petroleum, and chemical industries.
(7) Other energy boilers
Boilers that use nuclear energy, solar energy, geothermal energy, electric energy, etc. as energy sources.
4. Classification by combustion method
(1) Fire bed combustion (stratified combustion) boiler
A boiler in which fuel is laid on the grate for combustion.
(2) Fire chamber combustion (suspension combustion) boiler
A boiler in which fuel is injected into the furnace space and burns in suspension.
(3) Fluidized bed combustion (boiling combustion) boiler
The fuel is held up by the high-speed air flow sent from bottom to top on the air distribution plate, and it rolls up and down to burn the boiler.
(4) Cyclone furnace combustion boiler
Coarse pulverized coal or coal dust is driven by a powerful air flow in a horizontal or vertical cyclone to rotate and burn in a boiler with liquid slagging.
5. Classified by ventilation method
(1) Natural ventilation boiler
A boiler that uses the pressure head formed by the difference between the hot flue gas in the chimney and the outside cold air to overcome the flow resistance of air and flue gas.
(2) Mechanical blower boiler
A boiler in which only blower is installed in the boiler blower and induced draft system to overcome smoke and resistance.
(3) Mechanical induced-draft boiler
A boiler in which only induced-draft fans are installed in the delivery and induced-draft system of the boiler to overcome the resistance of the smoke and air ducts.
(4) Balanced ventilation boiler
A boiler in which the supply and induced draft fans are installed in the boiler's supply and induced air system to overcome the resistance of the air duct and the resistance of the flue respectively.
6. Classification by furnace flue gas pressure
(1) Negative pressure combustion boiler
A boiler in which the negative pressure of flue gas at the outlet of the furnace is maintained at 20 ~ 40Pa.
(2) Slightly positive pressure combustion boiler
A boiler whose flue gas gauge pressure at the outlet of the furnace is 2000 ~ 5000 Pa.
(3) Supercharged combustion boiler
A boiler whose flue gas gauge pressure at the outlet of the furnace is greater than 300kPa.
7. Classified by circulation method
(1) Natural circulation boiler
A boiler with a drum that uses the pressure generated by the difference in the density of the working fluid in the downcomer and the riser or in the boiler tube bundle to overcome the flow resistance of the pipeline and promote the circulating flow of the working fluid.
(2) The forced circulation boiler
A boiler with a boiler and a circulating water pump, which uses the pressure generated by the difference in the density of the working fluid in the circulation loop and the pressure provided by the circulating water pump to overcome the flow resistance of the pipeline and promote the circulating flow of the working fluid.
(3) Once-through boiler
A boiler without a drum, and the feed water passes through the heating surface to generate steam once the pressure provided by the water pump.
8. Classified by boiler structure
(1) Shell boiler
A boiler with a shell containing water and steam, and the heating surface of the flue pipe arranged in the shell.
A boiler with a combustion chamber arranged inside the shell is called an internal combustion shell boiler; a boiler with a combustion chamber arranged outside the shell is called an external combustion shell boiler (ie water-fire tube boiler).
(2) water-tube boiler
A boiler in which the water, steam, steam-water mixture and other working fluids flow in the tube to be heated, and the high-temperature flue gas scours and releases heat outside the tube.
9. Classified according to the working fluid used
(1) Ordinary working fluid boiler
Ordinary working fluid boiler refers to a boiler that uses water as a working fluid.
(2) Special working fluid boilers
Special working fluid boilers refer to boilers that use mercury, mineral oil and high-temperature organic heat carriers as working fluids.
10. Classified by boiler layout
(1) Boiler with vertical drum.
A boiler whose drum longitudinal centerline is parallel to the front and rear centerlines of the boiler.
(2) Boiler with horizontal drum.
A boiler in which the longitudinal centerline of the drum is perpendicular to the front and rear center of the boiler.
11. Classified by boiler delivery form
(1) Quick-installed boiler
The boiler body is a fully assembled boiler.
(2) Assembled boiler
The boiler body is manufactured into several assemblies when it leaves the factory, and assembled into the whole boiler at the installation site, which is called an assembled boiler.
(3) Bulk boilers
When the boiler body leaves the factory, a large number of parts and components are manufactured and installed at the installation site according to the design drawings of the boiler factory to form the entire boiler, which is called a bulk boiler.
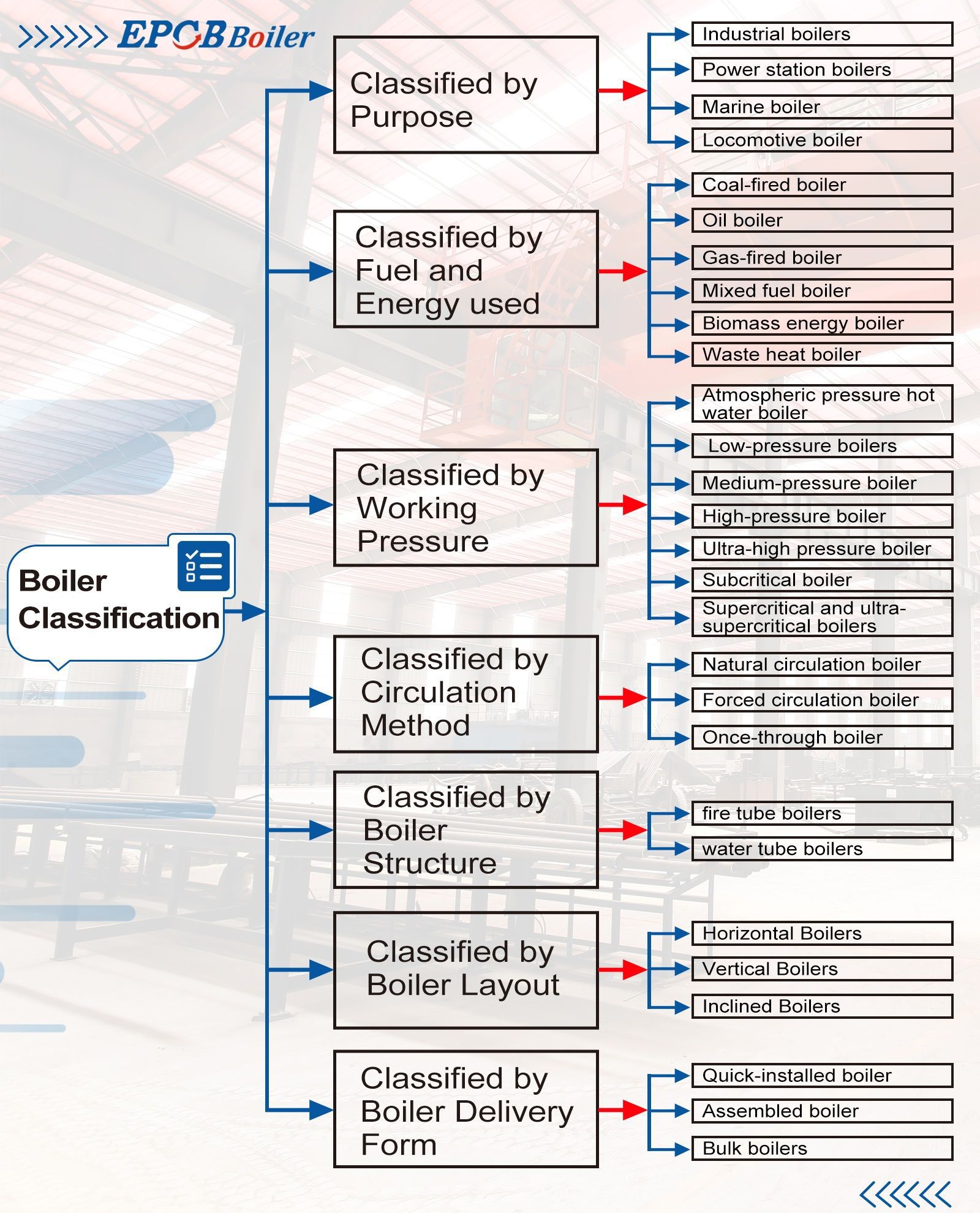
Boiler Working Process
The working process of the boiler can be roughly divided into two major processes at the same time: the process in the furnace and the process in the boiler. The former includes the fuel combustion process and the heat transfer process in the furnace on the flue gas side of the heating surface: the latter includes tension. The heat transfer process between the metal and the working fluid, the heating, evaporation and overheating process of the working fluid, the flow process of the working fluid and the thermochemical processes on the working fluid side (such as steam quality, salt precipitation, heating surface fouling and corrosion, etc. ).
1. In-furnace process
Coal into the boiler coal from coal storage means, direct coal coal bin by gravity into the coal pipe through the slide hopper coal furnace, and then slowly fell forward movement of the chain guard row, through the gate into the coal combustion room.
The air required for fuel combustion is forced into the air preheater by the blower, and enters the segmented air supply bin under the grate after the temperature rises, and then fully contacts and mixes with the coal on the grate to carry out a strong combustion reaction.
The high-temperature flue gas transfers heat to the water or steam-water mixture laid in the water-cooled wall around the combustion chamber by means of radiation heat exchange. Then, the high-temperature flue gas passes through the slag condensing tube through the smoke window (furnace exit), flushes the steam superheater, and flushes the boiler tube bundles laterally along the fire (smoke) wall, and transfers heat to the convective heating surface by means of convective heat transfer.
The working fluids such as steam, water, and soda-water mixture in the tube bundle; the flue gas whose temperature gradually decreases along the way enters the heating surface of the tail, flushes the economizer, and transfers part of the heat to the working fluid-water in the tube by means of convective heat exchange. The air enters the air preheater tube, flows and washes in the tube, and transfers heat to the working fluid flowing outside the tube in a convective heat exchange mode. The heated air enters the furnace to strengthen the combustion in the furnace and increase the furnace temperature.
Thereby improving the thermal efficiency of the boiler. So far, the temperature of the flue gas has dropped to the economical flue gas temperature, leaves the boiler body, and is discharged into the atmosphere through the dust collector, induced draft fan, flue, and chimney. The ash and slag generated by combustion are sent to the slag yard through the ash removal device.
2. Process in the pot
The feedwater that has been processed by the water treatment system and meets the boiler water quality requirements is sent to the economizer by the feedwater pump through the water supply pipeline. The water absorbs the heat of the flue gas in the tail flue in the economizer, and the preheated feedwater enters the upper drum. The downcomer flows into the radiant heating surface (water wall) through the header at the lower part of the water wall. The water in the water wall absorbs the high-temperature radiant heat in the furnace to form a steam-water mixture and flows into the upper boiler tube;
The same process is also carried out in the boiler tube bundle. The boiler water in the upper drum flows down the lower drum along the weakly heated tube bundle, and the lower drum undergoes the stronger heated tube bundle to form a steam-water mixture and then flows back to the upper drum.
The steam-water mixture is separated in the upper drum through the steam-water separator. The saturated steam is sent to the steam superheater from the upper part of the drum. The steam exchanges heat in the steam superheater with the high-temperature flue gas outside the tube to absorb the heat of the high-temperature flue gas. After that, superheated steam is formed, and reaches the rated superheated steam temperature through the steam temperature regulating device.
The qualified steam is merged into the superheater outlet header, enters the sub-cylinder through the main steam valve, and then is distributed to the heat users.
Conclusion
Through the above process, classification and working process of the boiler, I believe you have a preliminary understanding of the boiler, I hope this will help you.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler