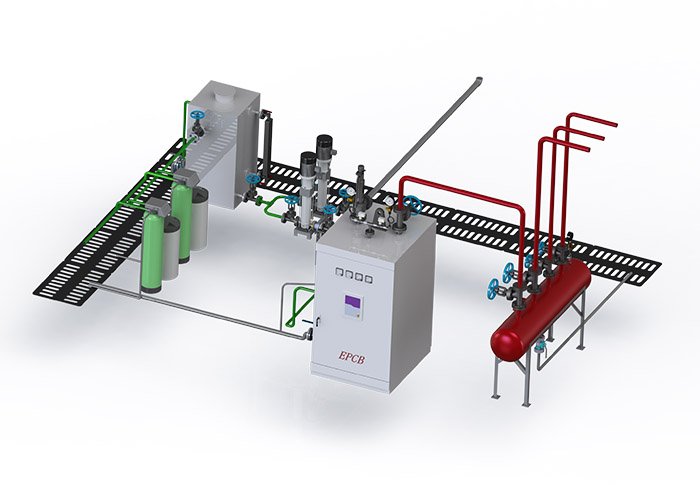
Boiler feed water treatment and boiler water quality control are one of the important measures to ensure the safe and economic operation of the boiler. In the operation of industrial boilers, due to improper treatment of boiler feed water, the phenomenon of scaling on the heating surface is not uncommon, thereby reducing boiler thermal efficiency and increasing energy consumption; in some cases, it can also cause heating surface to overheat, which seriously affects boiler’s service life. Therefore, strengthening boiler feed water treatment and boiler water quality control is of great significance to boiler safety and economic operation.
Industrial boiler water treatment generally adopts two methods: out-of-boiler water treatment and in-boiler water treatment.
Let us understand the purpose and technical requirements of boiler water treatment first , as well as the advantages and disadvantages of the two water treatment methods.
Water Treatment Purpose | Water Treatment Technical Requirements |
1. Keep the metal heating surface of the boiler free of scale or thin scale operation. 2. Reduce the deposits formed in the boiler drum and header. 3. Prevent all kinds of corrosion on the metal water vapor side of the boiler. 4. Control the content of impurities such as salt and alkali in boiler water to reduce pollution and heat loss. 5. Ensure the output of qualified quality heat medium (steam or hot water). | 1. Purification of water, separation of suspended solids, colloids and impurities 2. Water softening 3. Reduce alkalinity 4. Desalination 5.Eliminate dissolved oxygen and other gases |
Treatment method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applicable boiler type |
Out-of-boiler treatment | The treated water quality is good, the sewage discharge is small, and the water quality is easy to control. | Larger investment and more operation and management costs. | Larger, low-pressure water tube boiler |
In-boiler treatment | The equipment cost is low, the investment is low, the operation and management is simple. | The water quality is poor, it is difficult to control, and the sewage discharge is large. | Small, low-pressure steel boiler |
Out-of-boiler water treatment
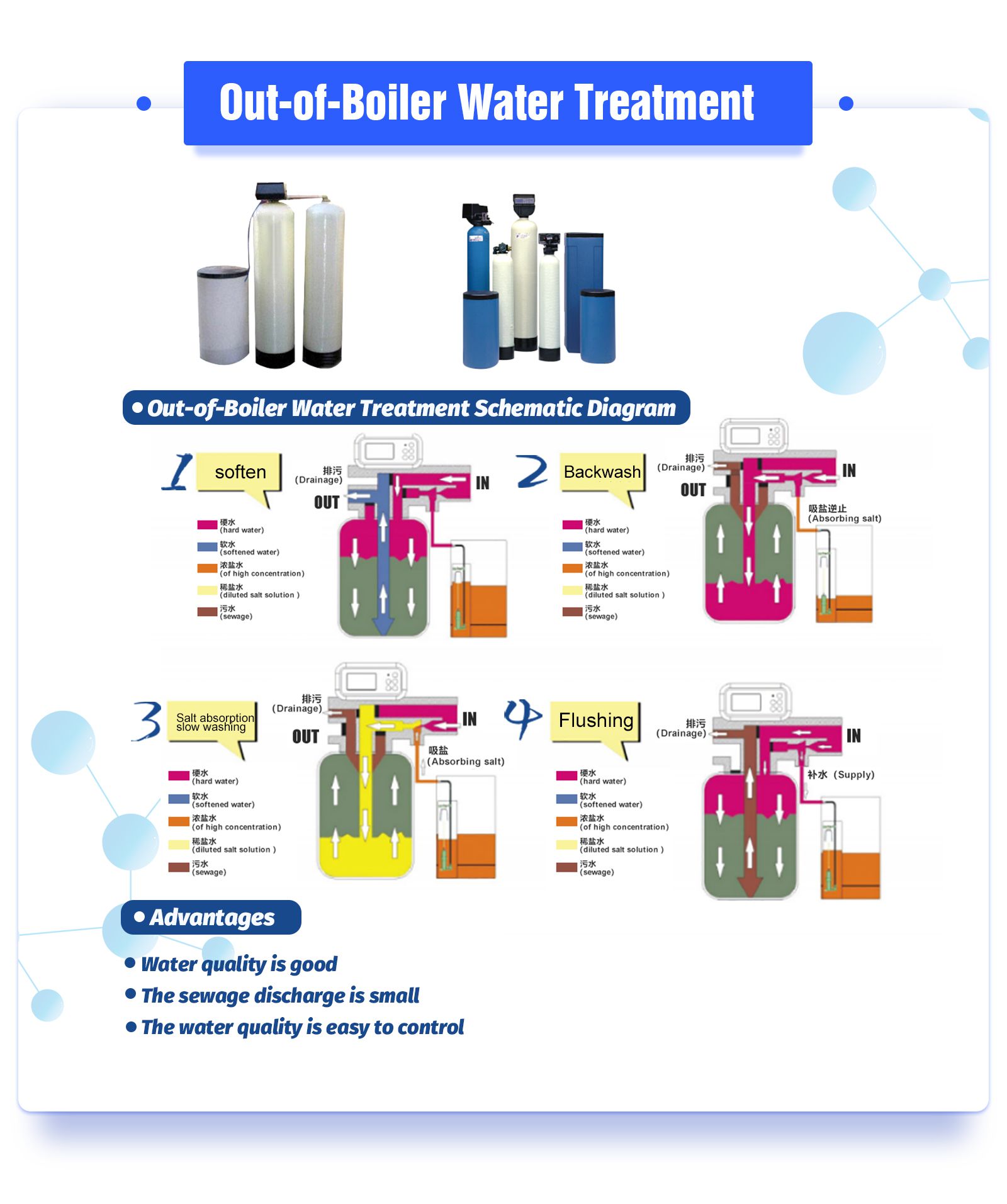
Out-of-boiler water treatment mainly refers to a series of processes in which water is softened before entering the boiler.
I. Boiler feed water softening
1. Boiler feed water softening method outside the boiler
1) Lime-sodium ion exchange.
2) Hydrogen-sodium ion exchange.
3) Ammonia-sodium ion exchange.
4) Chemical desalination.
2. Types of ion exchangers
Ion exchanger | Type |
Inorganic ion exchanger | Sea green sand, changling clay, artificial zeolite, etc. |
Organic ion exchanger | Sulfonated coal, ion exchange resin |
II. Sodium ion exchange softening
At present, the most used systems are single-stage sodium series and two-stage sodium series.
1. Single-stage sodium tandem system
Features:
1) Single-stage sodium is generally suitable for raw water with a total hardness of less than 5mmol/L, and the residual water hardness can be less than 0.03mmol/L.
2) The equipment is simple, the management is convenient, and the land occupation and equipment investment are less and less expensive.
3) Set up two exchangers, one for operation and one for standby, so as to ensure the quality and quantity of water into the boiler.
4) During the operation of the single-stage sodium tandem system, water quality monitoring must be strengthened to prevent excess water from entering the water supply system.
2. Two-stage sodium series system
Features:
1) Two-stage sodium is suitable for raw water with a total hardness of less than 5mmol/L, and the residual water hardness can reach 5-10pmol/L.
2) The total salt consumption of the whole system is low.
3) Ensure the reliability of water supply.
4) Only one secondary sodium tank can be installed.
5) Try not to interchange and mix primary and secondary sodium, because the interchange and mixed use not only complicates pipelines and valves, but also easily causes misoperation by operators. Moreover, once the valve is not strict and pollutes the water quality, it is difficult to find and solve it in time.
6) The installation and layout of equipment should take into account the normal water supply in case of overhaul or failure.
7) The general softening system is equipped with a high-level water tank to store the softened water for later use. In order to prevent the high-level water from flowing back when the softener stops running, a check valve should be installed between the softener outlet and the high-level water tank.
III. Fixed bed ion exchange softening
Fixed-bed ion exchangers are divided into two types: co-current regeneration and counter-current regeneration according to the regeneration mode.
The fixed-bed countercurrent regenerative ion exchange system is a regeneration method widely used at home and abroad. Compared with the regeneration of the downstream regenerative ion exchange system, it has the following obvious advantages:
1) The effluent quality is good.
2) Less consumption of regeneration liquid (low salt consumption).
3) Low water consumption during regeneration.
4) Strong practicability for raw water during operation.
5) The discharge concentration of waste liquid during regeneration is low, which reduces environmental pollution.
In-boiler Water treatment
The water treatment in the boiler is to add chemicals and organic colloids (such as tannin extract) into the pot water, so that the calcium and magnesium salts form loose, non-cohesive slag substances to precipitate out, and the sewage is discharged out of the pot regularly.
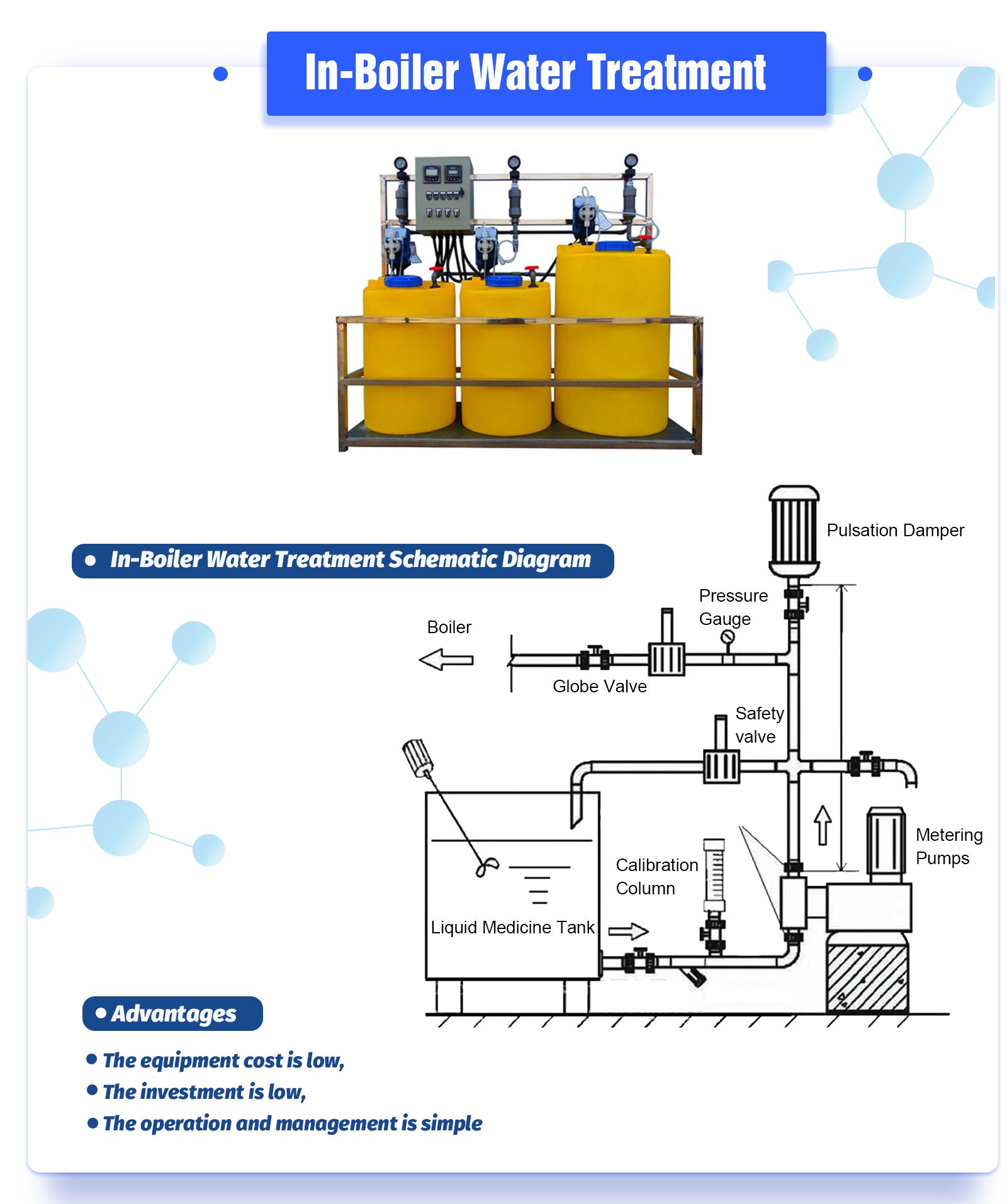
I. Commonly used medicine
Several commonly used agents: soda ash (Na2PO4.12H20), trisodium phosphate (Na3PO4.12H20), comprehensive water softener (three sodium and one glue), sodium humate and graphite.
II. Dosing device
1. Dosing pump
2. Water injector
3. Differential pressure dosing tank
III. Dosing Method
1. There are two main ways of dosing: continuous dosing and intermittent dosing.
Dosing Method | Advantages and Disadvantages | Application Scope |
Continuous Dosing Uniformly | conducive to the safe operation of the boiler and easy for automatic control, but the equipment is more complicated. | It is suitable for large and medium-sized boilers. |
Intermittent | chemical dosing equipment is simple, but the concentration of the boiler water chemical liquid fluctuates greatly. | Suitable for small low-pressure boilers |
2.operation management matters needing attention
1) Insist on timely and reasonable dosing, according to changes in raw water quality, boiler operating load, sewage and boiler water quality, and dosing on time and on time every day and every shift. For intermittent dosing, the dosing time should not be too long.
2) Adhere to frequent and reasonable sewage discharge. The bottom drain can promptly drain the loose slag material generated by the addition of the pot to the outside of the pot to prevent the formation of secondary scale, and insist on reducing the discharge and discharging frequently.
3) Strengthen the laboratory supervision of the pot water, and be aware of it, especially to maintain the pH value of boiler water = 10~12.
4) Regular cleaning. The water slag material generated by the addition of medicine in the boiler cannot be completely discharged through the bottom of the sewage. It accumulates and deposits more and more, which will threaten the safe operation of the boiler.
In addition to the two industrial boiler water treatment methods, out-of-boiler water treatment and in-boiler water treatment, boiler feed water deoxygenation is also one of the important technologies to ensure the quality of boiler feed water.
Boiler Feed Water Deaeration
Because oxygen and carbon dioxide, especially oxygen, are dissolved in the boiler water, in the boiler body and the soda system, under the conditions of high temperature, pressure and electrolyte, electrochemical corrosion occurs quickly, and the consequences are serious. Therefore, deaeration of feed water is an indispensable and important means to ensure the safe and economic operation of the thermal system.
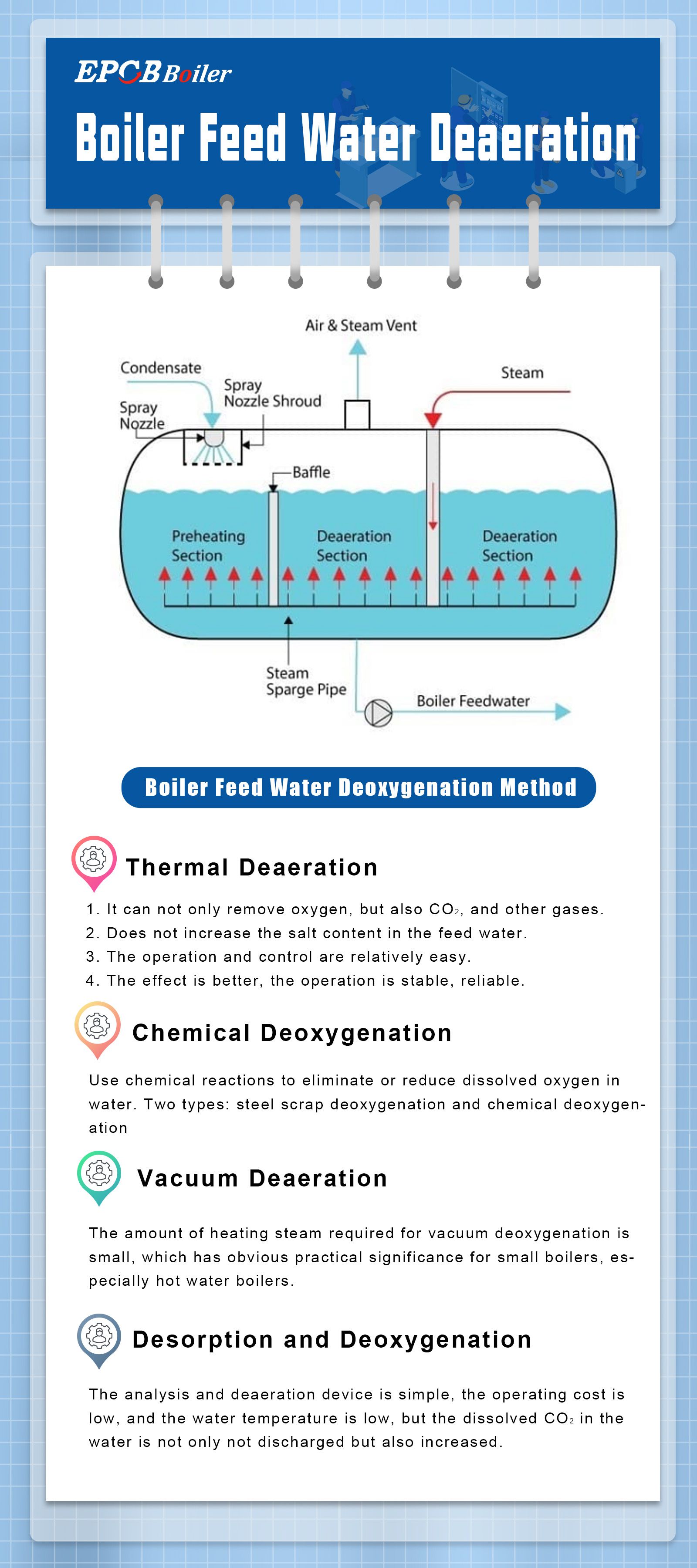
The methods of deoxygenating water supply are:
1) Thermal deaeration.
2) Chemical deaeration.
3) Vacuum deaeration.
4) Desorption and deaeration.
I. Thermal Deaeration
Thermal deaeration is to maintain a pressure slightly higher than atmospheric pressure (0.02MPa) in the deaerator, and heat the feed water to the saturation temperature (104.25°C) under the corresponding pressure, so that the escaped gas and a part of the remaining steam can be discharged in time. Do not discharge too much steam and cause waste.
1.Advantages and disadvantages of thermal deaeration:
Advantages | Disadvantages |
1.It can not only remove oxygen, but also CO2, and other gases. 2.Not increase the salt content in the feed water. 3.The operation and control are relatively easy. 4.Compared with other methods, the effect is better, the operation is stable, reliable. | 1.Large gas consumption. 2.The temperature of the feed water entering the economizer is high, which is not conducive to making full use of the waste heat of the flue gas, resulting in large exhaust loss.
|
2.Operation of deaerator and matters needing attention
1) The inlet water temperature of the deaerator should not be too low, generally around 80°C. Otherwise, it takes a long time to heat to the saturation temperature under the corresponding pressure in the deaerator, it is difficult to achieve the expected deaeration effect, and water hammer is prone to occur.
2) Stable pressure and temperature must be maintained in the deaerator, and its working condition parameters should be: working pressure 0.02MPa, temperature 104~106℃.
3) Proper exhaust volume must be guaranteed on the deaerator head so that the resolved oxygen can be discharged in time. The exhaust valve should maintain the best opening, and excessive opening will cause steam waste.
4) In order to ensure the reliable and economical operation of the deaerator, the pressure, temperature, and water level of the deaerator should be automatically adjusted as much as possible. Manual adjustment is often difficult to achieve the desired effect.
5) The deaerator must continuously and stably feed water and operate continuously. When several deaerators are operated in parallel, water can be added to one in a centralized manner, and the water inflow of several deaerators at the same time will often destroy the stability of operation.
6) When several deaerators are running in parallel, a steam-water balance pipe must be installed. In order to eliminate the unbalanced phenomenon of the water level and pressure of each deaerator.
7) Laboratory inspection and supervision must be strengthened for deoxygenated water, and continuous and automatic instrument monitoring is best to prevent unqualified water from entering the boiler. ...
8) Too high temperature of the water outlet of the deaerator will easily cause the water to vaporize in the feed water pump, and will also cause the economizer inlet temperature to be too high and reduce the economizer utilization rate. Therefore, the outlet water of the deaerator should pass through a heat exchanger and use low-temperature softened water to cool down.
II. Chemical Deaeration
Chemical deoxygenation is the use of chemical reactions to eliminate or reduce dissolved oxygen in water. There are two methods for deoxidizing steel scraps and deoxidizing chemicals.
1. Deaeration of steel scraps
This method is to flow water through a steel chip filter to oxidize the steel chip and consume the oxygen in the water.
2. Deaeration of medicament
This method is to add chemical agents to the water to dissolve and oxidize in the water to generate non-corrosive substances to obtain the purpose of deoxygenation. If Na2SO4 is injected, the following reactions occur:
2Na2SO3+O2→2Na2SO4
III. Vacuum Deaeration
Vacuum deaeration refers to deaeration under atmospheric pressure. Its principle is similar to that of thermal deaeration. That is, at a certain temperature (such as normal temperature), the boiling point of water decreases with the pressure on the water surface. Dissolved oxygen and other gases are removed. The temperature of the outlet water for vacuum deaeration can be 3~60℃, so the amount of heating steam required for vacuum deaeration is small, which has obvious practical significance for small boilers, especially hot water boilers.
Attention in the operation of vacuum deaeration
1) The discharge of the gas mixture of the vacuum deaeration head is mainly realized by the vacuum degree caused by the ejector or vacuum pump in the deaeration head, so the quality of its performance is very important.
2) The inlet water temperature should generally be above 15°C, which should be 0.5~1°C higher than the boiling point of the deaerator head under the corresponding vacuum to maintain a certain degree of superheat, so that part of it is vaporized and the rest is in a boiling state.
3) Since the vacuum deaeration works under negative pressure, the tightness of the entire system must be maintained. The pipeline should be welded, the flanges should be isolated with rubber gaskets, and the pump shaft seal and valve stem should be sealed with water to prevent Air leak.
4) In order to maintain a certain positive pressure in front of the feed water pump and prevent air leakage under negative pressure and increase the dissolved oxygen, the deaeration water tank must be arranged at a high level rather than on the same floor as the water pump.
IV. Desorption and Deoxygenation
Desorption and oxygen removal are based on the principle that the solubility of oxygen in water is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas on the water surface, and the partial pressure of oxygen in the gas is proportional to the concentration of oxygen in the gas. When oxygen-containing water and oxygen-free gas are strongly mixed, the oxygen dissolved in the water will diffuse into the oxygen-free gas to achieve the purpose of deoxygenation.
The desorption and deoxygenation device sprays water into small mist particles, which meet with the heated charcoal to take away the oxygen in the water. The deoxygenated water enters the closed water tank and then is sent to the boiler. In the past, charcoal heating used the boiler itself, but now some of them use electric heating alone. This method is simple in equipment, low in operating costs, and low in water temperature, but the dissolved CO2 in the water is not only not discharged but will increase, and it is not used much.
After the boiler has been running for a long time, scale and rust problems will inevitably appear. In order to make the boiler system operate in an optimized state, the water system of the boiler system must be specially treated: remove the scale in the boiler.
Remove Boiler Scale
The method of removing scale in the pot and its advantages and disadvantages.
Descaling method |
| advantages and disadvantages |
Mechanical descaling |
| The descaling method is simple and easy, but the labor intensity is high, the descaling is incomplete, and the boiler metal is wasted. Due to the limitation of the boiler structure, the pipe with a small curvature cannot be carried out |
Chemical descaling | Alkaline boiling descaling | is simple, reliable, and less corrosive, but the descaling effect is poor, the cooking time is long, and the chemical consumption is large |
Pickling and descaling | operation requires relatively high, corrosive, but the descaling effect is better. The pickling process requires a lot of water, so a combination of dynamic circulation and dynamic and static should be used. |
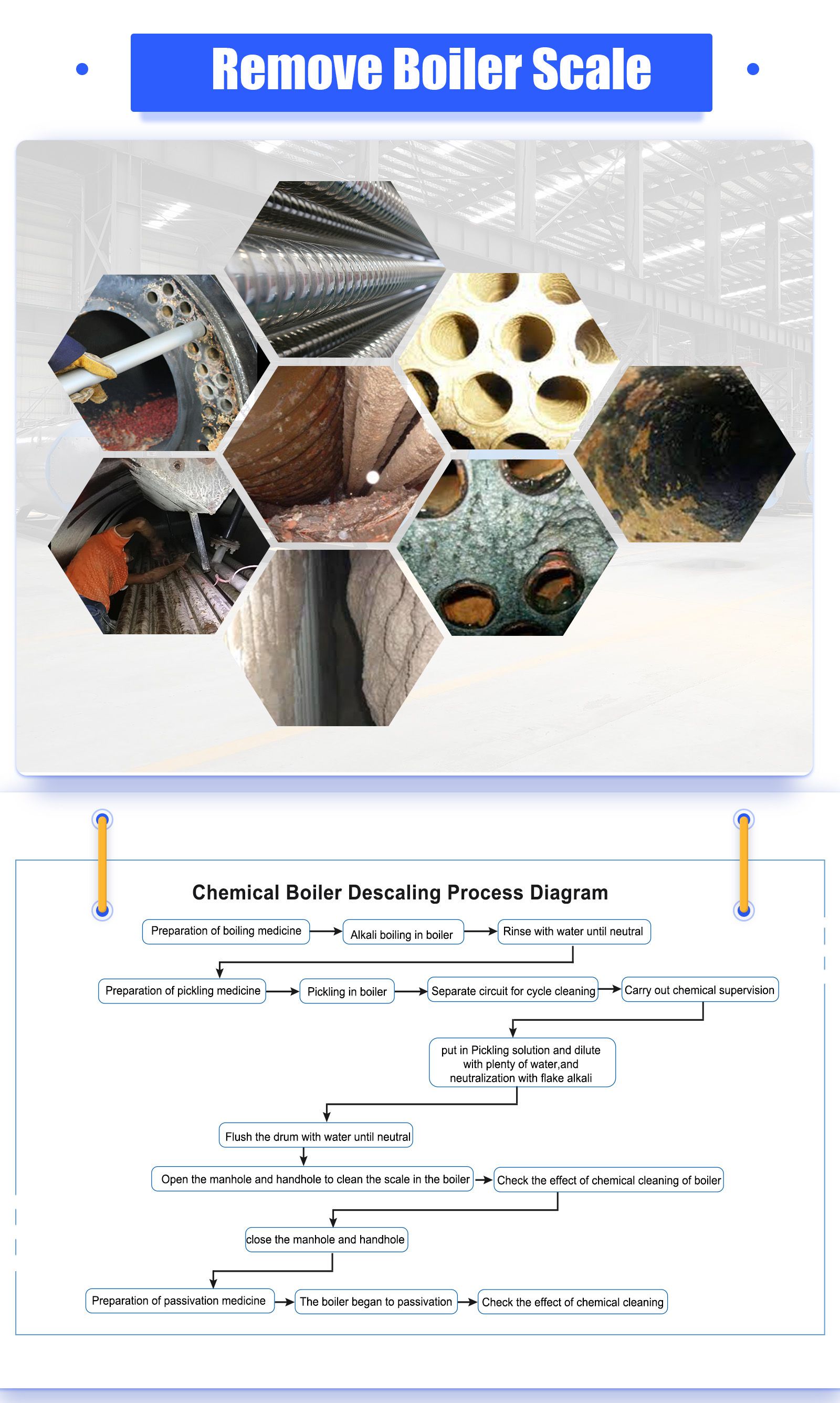
I. Mechanical descaling
Mechanical descaling is to use tools such as hammer, shovel, scraper, wire brush or electric pipe cleaning when the boiler is out of service.
II. Chemical descaling
1. Alkali boiling and descaling
Alkali boiling descaling can loosen and soften the scale, so it is often used as a pretreatment for pickling descaling and mechanical descaling.
Alkaline boiling descaling dosage
Agent name | Adding amount (kg/t boiler water) | Mass concentration (%) |
Soda ash (Na2CO3) | 10-20 | 1-2 |
Caustic soda (NaOH) | 2 | 0.2-0.4 |
Trisodium phosphate (Na3PO4 12H2O) | 3-5 | 0.3~0.5 |
Note: The alkali-cooking and descaling time should generally be no less than 24h (steel furnace without pressure).
2. Pickling and descaling
At present, the most economical, effective, simple and rapid descaling method at home and abroad is pickling descaling.
1)commonly used pickling and descaling and corrosion inhibition
Acid for pickling | Hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid, chromic acid, hydrofluoric acid |
Corrosion inhibitor | "Ruo Ding" |
The pickling temperature should be 59℃, and the pickling time should generally not exceed 6h.
2) When the boiler is pickled, the pickling solution should be prepared according to the thickness of the scale.
Concentration and dosage of acid
Scale thickness /mm |
| Mass concentration of hydrochloric acid | 31%HCL |
| 29%HCL |
| 27%HCL |
| 25%HCL |
|
Hot water boiler | Steam boiler | (%) | Acid volume | Water volume | Acid volume | Water volume | Acid volume | Water volume | Acid volume | Water volume |
<2 | <1 |
| 19.3 | 80.7 | 20.7 | 79.3 | 22.2 | 778 | 24.0 | 160 |
2-6 | 1-2 | 8 | 25.9 | 74.1 | 27.6 | 724 | 29.7 | 70.3 | 32.0 | 68.0 |
>0 | 2-5 | 10 | 32.3 | 67.7 | 34.5 | 69.5 | 37.1 | 62. | 40.0 | 60.0 |
5-10 | 12 | 38.7 | 61.3 | 41.4 | 58.6 | 44.5 | 55.5 | 48.0 | 52.0 |
>10 | 15 | 48.4 | 51.6 | 51.6 | 48.3 | 51.7 | 44.5 | 60.0 | 40.0 |
3) Matters needing attention in pickling.
① The water vapor pipeline connecting the pickling furnace and the operating furnace should be separated by blind plates to prevent the acid and alkali liquid from the pickling process from entering the operating furnace, causing serious consequences.
②Hydrogen generated in the pickling process must be discharged to a safe place to prevent explosion.
③In the pickling process, laboratory supervision must be strengthened, especially at the beginning and end of pickling, sampling and testing should be done frequently.
④Pickling staff should be familiar with the process, methods and key points of the entire pickling process, and wear acid-proof protective equipment during operation to prevent acid from splashing on the skin, especially in the eyes.
⑤ The large amount of acid-base waste liquid produced in the pickling process must be neutralized and meet the sewage discharge standard before being discharged into the industrial sewage discharge system.
⑥The problems found in the pickling process and the data of the test must be carefully recorded.
Conclusion
With the development of the social market economy, boilers are widely used in production and life. Water is the “blood” of boiler power. A considerable number of boilers have problems of this kind due to water treatment work. If the boiler water quality does not meet the requirements of industrial boiler water quality, serious boiler scaling will result, which will cause work accidents and energy resources. Big waste. Doing a good job of water treatment is a vital task to ensure the safe, efficient and economical operation of the boiler. If you have any questions about the use of the boiler, please contact EPCB.
EPCB, your private boiler system expert!
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler