When selecting industrial boilers, water tube boilers and fire tube boilers are the two main types. Water tube boilers are suitable for high-pressure and large-capacity applications, such as power plants, while fire tube boilers are more applicable to medium-pressure and fluctuating load scenarios, such as food processing. According to industry data, water tube boiler efficiency can reach 85%-95%, while fire tube boilers are at 75%-85%.
In this article, we will explore the key differences between water tube boilers and fire tube boilers, including design features, performance characteristics, and application suitability, to help you make an informed decision.

What Is a Water Tube Boiler?
The core design of a water tube boiler lies in water flowing through the tubes, with the heat source surrounding them from the outside. This structure supports high-pressure operation and is widely used in large-scale industrial settings. Based on reliable data, the efficiency of water tube boilers typically ranges between 80%-92%, and can approach 95% under optimized conditions. For example, in the power sector, water tube boilers can efficiently handle peak and valley loads, providing stable and reliable steam supply.
To further enhance performance, water tube boilers incorporate a manifold system that enables parallel water flow through multiple paths. This design not only improves flow rates but also significantly optimizes heat exchange performance, making it particularly suitable for high-pressure steam demand scenarios. Additionally, the precise layout of the tubes maximizes the heat contact surface, reducing energy waste.
In the operation of a water tube boiler, water flows along the interior of the tubes, which are arranged in a precise array to optimize heat absorption. The manifold mechanism ensures even distribution of water across the tubes, thereby enhancing overall system efficiency. This flow mode not only promotes rapid heating but is also especially suitable for variable load conditions. For instance, in a transformation project at an oil processing plant, this configuration reduced equipment preheating time from half an hour to a quarter of an hour, significantly improving operational efficiency and smoothness.
What Is a Fire Tube Boiler?
Unlike water tube boilers, the design of fire tube boilers allows combustion-generated hot gases to pass through the tubes, with water enveloping them from the outside. This layout is relatively straightforward and commonly seen in smaller-scale applications or scenarios with less stringent operational requirements. The efficiency of fire tube boilers typically falls between 70%-85%. Although slightly lower than water tube boilers, through modern technological improvements, their performance can rival water tube boilers in certain conditions. In the food industry, fire tube boilers are favored for their excellent heat storage capacity, providing stable support for processing needs.
Fire tube boilers are renowned for their simplicity and ease of use, typically employing fewer but larger-diameter tubes. In recent years, technological advancements have further optimized their design, such as reducing water content to expand heating range and improve modulation performance. This simplicity not only lowers maintenance difficulty but also facilitates routine upkeep, though special attention is needed for cleaning inside the tubes to ensure long-term efficient operation.
In the operation of a fire tube boiler, heat transfer occurs as combustion gases flow through the tubes, conducting energy to the surrounding water body. The design focuses on expanding the tube-water interface to promote efficient heat energy transfer. This heat transfer method performs particularly well under stable load conditions.
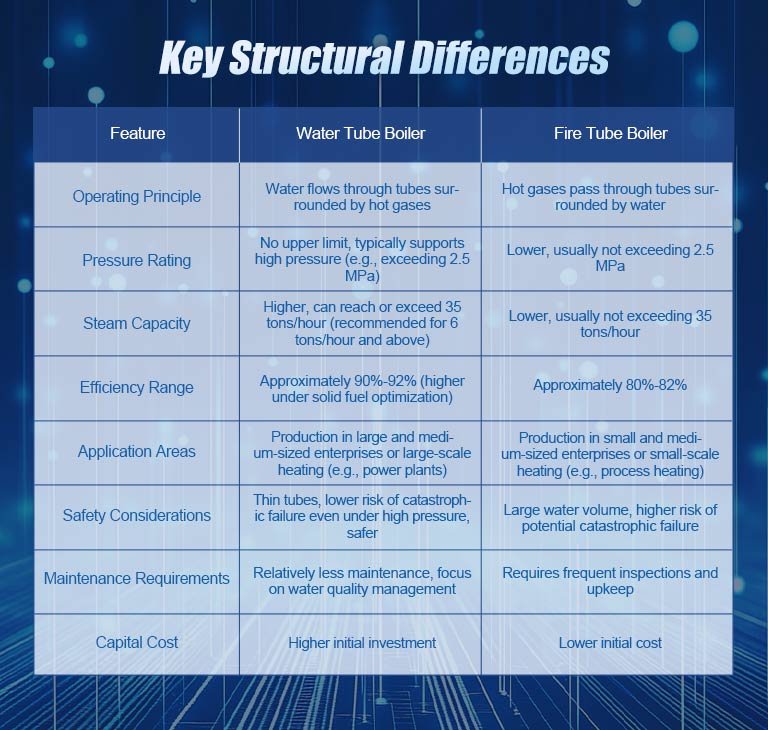
Key Structural Differences
The fundamental divergence between the two types of boilers stems from the relative positions of the heat source and water: in fire tube boilers, hot combustion gases pass through tubes surrounded by water; whereas in water tube boilers, water flows through tubes enveloped by hot gases. This basic design difference leads to a series of subsequent distinctions, such as fire tube boilers preferring low-pressure heating applications, while water tube boilers, due to their superior thermal efficiency and large steam output, are more suitable for high-pressure power generation fields. Other differences also involve water content, footprint, complexity, and heat surface arrangement. The following table summarizes these points for easy visual comparison:
Feature | Water Tube Boiler | Fire Tube Boiler |
Operating Principle | Water flows through tubes surrounded by hot gases | Hot gases pass through tubes surrounded by water |
Pressure Rating | No upper limit, typically supports high pressure (e.g., exceeding 2.5 MPa) | Lower, usually not exceeding 2.5 MPa |
Steam Capacity | Higher, can reach or exceed 35 tons/hour (recommended for 6 tons/hour and above) | Lower, usually not exceeding 35 tons/hour |
Efficiency Range | Approximately 90%-92% (higher under solid fuel optimization) | Approximately 80%-82% |
Application Areas | Production in large and medium-sized enterprises or large-scale heating (e.g., power plants) | Production in small and medium-sized enterprises or small-scale heating (e.g., process heating) |
Safety Considerations | Thin tubes, lower risk of catastrophic failure even under high pressure, safer | Large water volume, higher risk of potential catastrophic failure |
Maintenance Requirements | Relatively less maintenance, focus on water quality management | Requires frequent inspections and upkeep |
Capital Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial cost |
Water Volume | Less (4-8 times that of fire tube) | More, providing better heat retention |
Footprint | Larger, typically with dual-drum slender structure | Smaller, typically with single-drum thick and large structure |
Startup Time | Faster (5-15 minutes) | Slower (30-60 minutes) |
Heating Method | High-temperature flue gas in the furnace directly heats water inside the tubes | High-temperature flue gas inside the tubes heats water in the drum |
Water Quality Requirements | Higher, requires strict water treatment | Lower, greater tolerance |
Steam Temperature | Saturated steam up to 400°C | Saturated steam up to approximately 226.04°C |
Boiler Operation | More complex operation, requires more professional operators | Simpler operation, requires fewer operators |
Fuel Adaptability | Suitable for various coals, biomass, and other solid fuels | Suitable for various coals, biomass, and other solid fuels |
Boiler Structure Details | Dual-drum slender, water tubes thin and dense covering the furnace, no title design | Single-drum thick and large, fire tubes dense covering inside the drum, no title design |
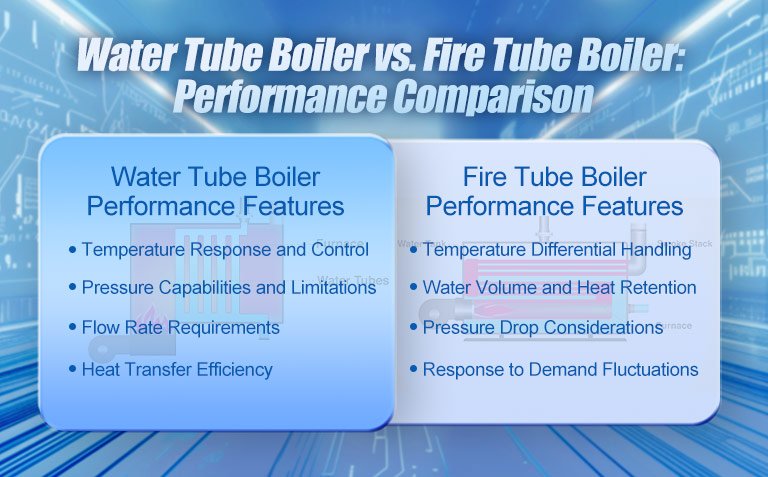
Water Tube Boiler vs. Fire Tube Boiler: Performance Comparison
The performance comparison between water tube boilers and fire tube boilers primarily revolves around their unique advantages in industrial demands. Each has its own focus and is suitable for different application scenarios, showing significant differences especially under solid fuel conditions. The following is a detailed analysis of the performance of both types of boilers:
Water Tube Boiler Performance Features
1. Temperature Response and Control: Water tube boilers are renowned for their rapid temperature adjustment and precise control capabilities, making them particularly suitable for scenarios with frequent load changes. This agility stems from the direct contact between water and the heat source, reducing response lag. For example, in an application at a textile factory, deploying a water tube boiler improved temperature control accuracy by 25%, significantly reducing defect rates.
2. Pressure Capabilities and Limitations: Water tube boilers support high-pressure operations with virtually no upper pressure limit, meeting high-pressure steam demands. However, this requires rigorous design and maintenance to avoid over-limit risks.
3. Flow Rate Requirements: Water tube boilers need to maintain stable water flow rates to ensure thermal efficiency and prevent equipment damage. This specification ensures even heat distribution and avoids local overheating.
4. Heat Transfer Efficiency: Due to water directly facing the heat source, water tube boilers have extremely high heat transfer efficiency. Under solid fuel conditions, their thermal efficiency can reach 90%-92%, performing exceptionally well in industrial applications.
Fire Tube Boiler Performance Features
1. Temperature Differential Handling: Fire tube boilers can withstand larger temperature differences, suitable for processes with variable temperatures. This buffering capability benefits from their ample water storage, effectively balancing temperature fluctuations.
2. Water Volume and Heat Retention: The large water capacity of fire tube boilers endows them with excellent heat storage capabilities, maintaining system stability even during brief heating interruptions. For example, in a case at a food factory, this feature prevented production interruptions, ensuring process continuity.
3. Pressure Drop Considerations: Due to their wide water channel design, fire tube boilers have smaller pressure losses, thereby reducing pump energy consumption and improving overall operational efficiency.
4. Response to Demand Fluctuations: Fire tube boilers have strong response capabilities to sudden load changes, especially during load reductions. This is due to their water mass advantage, making it particularly evident in HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) applications, where they can easily adapt to rapid changes in temperature and load.
Water tube boilers excel in high efficiency and quick response, suitable for high-pressure, high-temperature, and frequently changing load scenarios; while fire tube boilers stand out for their robustness and heat storage capabilities, applicable to larger temperature differences, stable loads, or small to medium-sized industrial needs. Both perform well under solid fuel conditions, allowing users to select the optimal solution based on specific requirements, achieving the best balance between performance and cost.
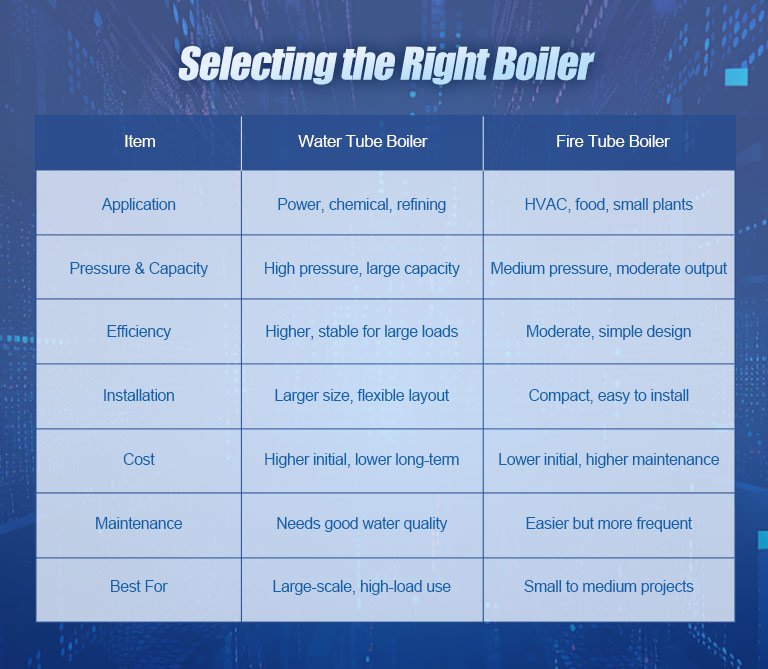
Selecting the Right Boiler
Selecting the appropriate boiler for your industrial application requires comprehensive consideration of the scenario, budget constraints, and efficiency demands.
Water tube boilers, with their high-pressure and high-steam capacity capabilities, are widely used in industries such as power, chemicals, and refining. Their flexibility and high efficiency can meet large-capacity needs, performing stably especially when burning solid fuels like biomass. Although they have a larger footprint, their dual-drum slender structure offers layout advantages in large venues.
In contrast, fire tube boilers are more suitable for medium-pressure demand industries, such as HVAC, food processing, and small power plants. Their design is simple, easy to install, and compact in footprint, making them especially suitable for space-limited locations.
In terms of cost, fire tube boilers have lower upfront investments, suitable for budget-constrained projects, while water tube boilers can recoup costs in long-term operations through higher efficiency and fuel utilization. Water tube boilers require strict water quality management and pipe cleaning, but with lower maintenance frequency and significant fuel-saving effects; fire tube boilers have simple maintenance procedures but higher pipe replacement costs.
Overall, water tube boilers are suitable for complex demands with high pressure and high loads, while fire tube boilers excel in economy and simplicity, ideal for small to medium-sized industrial applications. By evaluating industry needs, site conditions, and budget constraints, you can select the most suitable boiler to optimize production efficiency and economic benefits.
EPCB Boiler's Customized Industrial Boiler Solutions
With years of experience, EPCB Boiler is your reliable partner for customized industrial boiler solutions. Our expert team leverages extensive knowledge to help clients select the optimal boiler type based on specific industrial requirements, operational parameters, and budgets. We recognize that each industrial application has unique characteristics that may favor water tube or fire tube technology. Our comprehensive boiler selection approach considers pressure requirements, load profiles, space limitations, and long-term operational costs to deliver truly customized solutions.
Our manufacturing capabilities encompass water tube and fire tube designs across various fuel options, including oil-fired, gas-fired, coal-fired, biomass, and electric steam boilers. We provide complete turnkey solutions, including consultation, customized design, research and development, on-demand manufacturing, parts sourcing, and professional installation. Whether you need the high-pressure capabilities of a water tube boiler or the thermal stability of a fire tube boiler, we deliver solutions engineered for efficiency, reliability, and environmental responsibility.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific industrial boiler requirements and discover how our expertise in water tube and fire tube technologies can create your optimal steam generation solution.
FAQ
What Are the Main Differences Between Water Tube Boilers and Fire Tube Boilers?
In water tube boilers, water flows inside the tubes with the heat source outside; in fire tube boilers, hot gases flow inside the tubes with water enveloping them outside. This design difference directly affects pressure-bearing capacity and thermal efficiency, showing distinct performance especially in solid fuel applications.
Which Type of Boiler Is More Suitable for High-Pressure Applications?
Water tube boilers are more suitable for high-pressure applications, with a robust design and no pressure limit, capable of meeting high-pressure steam demands.
Is the Installation Cost of Fire Tube Boilers Lower Than Water Tube Boilers?
Yes, fire tube boilers have lower initial installation costs due to their simple structure, making them more economical. However, long-term maintenance and operational costs should be considered comprehensively.
How Do Condensing Boilers Improve Efficiency?
Condensing boilers recover residual heat from flue gases to preheat incoming water, reducing heat losses, with efficiency up to 95%.
What Is the Impact of Boiler Design on Heat Transfer?
Boiler design directly determines heat transfer efficiency. The complex tube layout of water tube boilers enables more efficient heat transfer, suitable for high-efficiency demands.
Can Water Tube Boilers Handle Larger Steam Demands?
Yes, water tube boilers have large capacity and flexible design, capable of efficiently handling large steam demands, performing exceptionally well especially in the power generation industry.
Do Fire Tube Boilers Have Specific Maintenance Requirements?
Fire tube boilers require regular inspections of tube sheets and tubes to ensure durability and safety. It is recommended to conduct two comprehensive overhauls annually.
How Does Boiler Footprint Affect Installation?
Footprint determines the boiler's applicability to the site. Water tube boilers have a larger footprint, suitable for large industrial venues; fire tube boilers are compact in design, more suitable for space-limited locations.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler