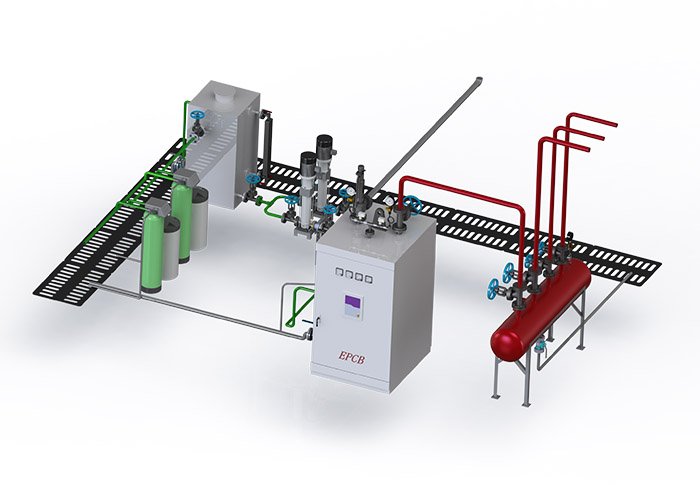
With the continuous progress of technology and environmental awareness, the application of electric boilers is becoming increasingly popular and sought after.
Traditional boiler systems typically rely on burning fuels, such as coal or natural gas. However, electric boilers use electrical energy as an energy source to meet household and commercial needs by converting electrical energy into heat. This clean, efficient energy conversion process makes electric boilers an environmentally friendly option, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and reducing negative environmental impacts.
In recent years, electric boilers have gradually started to be promoted and used in some industries.
Electric boiler development mileage
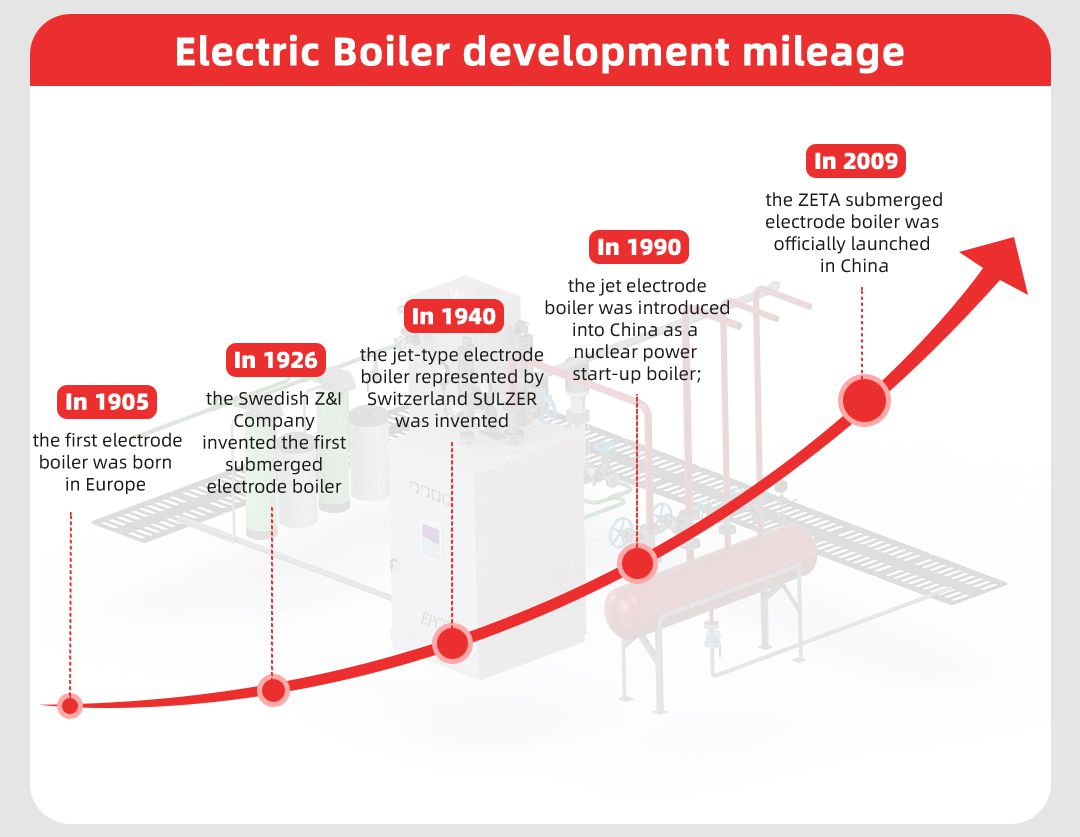
The application of electric boiler has been in foreign countries for many years, the first electrode boiler was born in Europe in 1905; in 1926, the first ZETA brand submerged electrode boiler was invented by Z&I company in Sweden, and the control accuracy was also improved, and high voltage (6~15kV) was used for direct power supply, which was called high voltage electrode boiler; in 1940, the jet electrode boiler represented by SULZER in Switzerland was invented; in 1990, the jet electrode boiler was introduced to China as a nuclear power starter boiler; in 2009, the ZETA submerged electrode boiler was officially launched in China again by the energy crisis. In 1940, the injection type electrode boiler represented by Swiss SULZER was invented; in 1990, the injection type electrode boiler was introduced to China as a nuclear power starter boiler; in 2009, ZETA submerged electrode boiler was officially launched in China again by the energy crisis.
Application of Electric Boiler

As the country attaches great importance to nuclear power business, China's nuclear power has gained a blowout development, electrode boiler as a high quality starter boiler for nuclear power plant also entered China, electrode boiler because of its high efficiency (for steam boiler, more than 99.9% of the input power can be converted into steam), no noise, environmental protection and no pollution, small footprint, fast starting speed, can work under low load for a long time, etc., so in Nuclear power plants have been widely used.
Electric boilers are mainly used in urban heating system for civil use. At present, China's urbanization continues to spread, urban heating area is also increasing, the situation facing energy saving and emission reduction is also more serious, energy supply diversification is has become China's security strategy, compared with coal, natural gas, biomass, electricity as a clean energy, has its own unique advantages. The centralized heating mode of electric boiler + energy storage using valley electricity as energy is consistent with the national policy of energy saving and consumption reduction, and electric boiler as the core equipment of heating system, it is worth to focus on research and promotion.
In industry, electric boilers are widely used as start-up boilers for thermal, wind and nuclear power plants and as auxiliary heat sources for solar heating systems, as well as providing high-quality steam and high-temperature hot water for production in a variety of industries.
Electric Boiler Classification and Working Principle
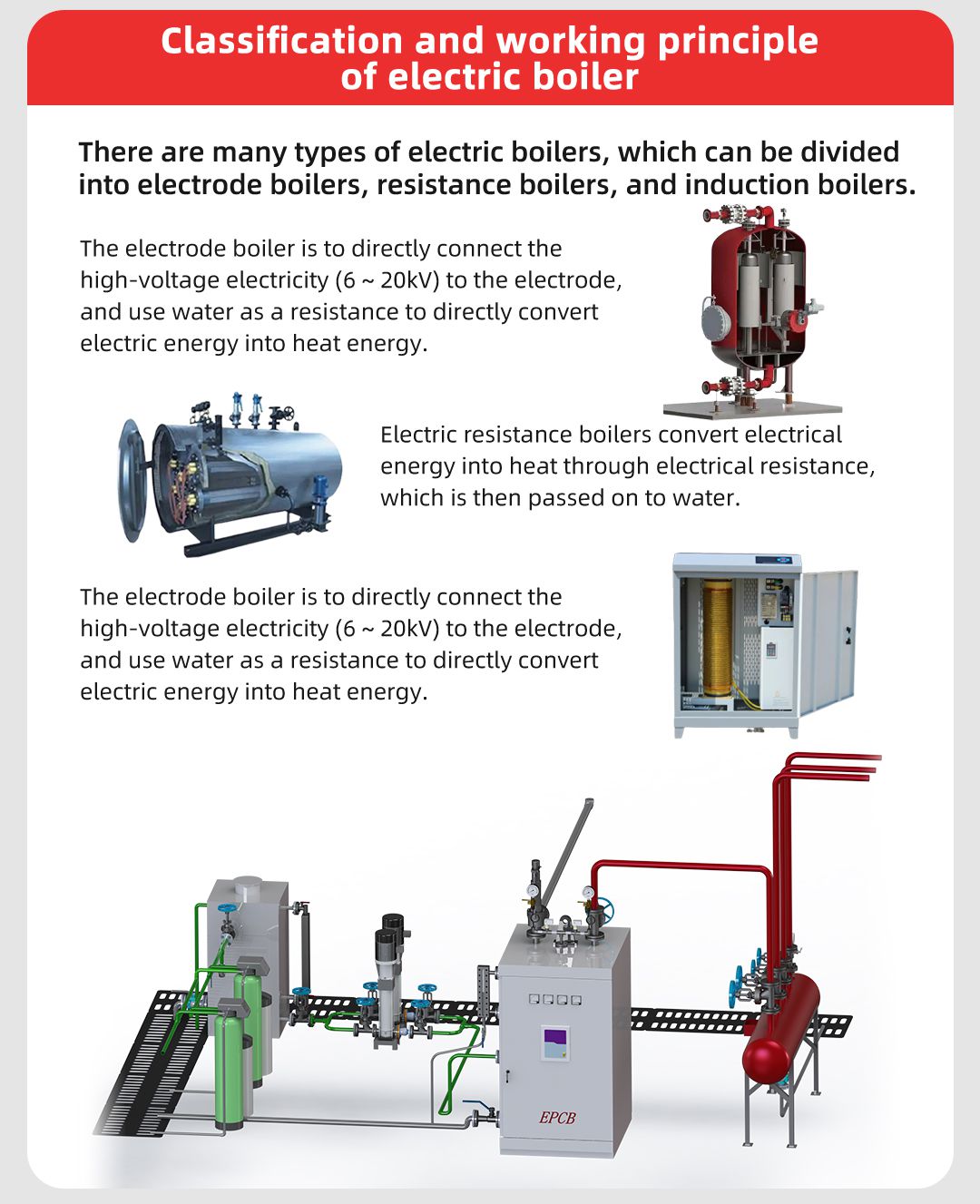
There are many types of electric boilers, which can be divided into electrode boilers, resistance boilers and inductive boilers according to their working principles. We would like to briefly introduce these three types of boilers in terms of the working principle of electric boilers.
Electrode boilers are electric boilers in which high-voltage electricity (6 to 20kV) is connected directly to the electrodes and water is used as a resistance to convert electrical energy directly into heat energy. The power load of a single electric boiler ranges from 4 to 80MW;
Electrode boilers are mainly classified into submerged and jet type. The resistance boiler converts electrical energy into heat energy through electrical resistance and then transfers it to water. The power load of single boiler ranges from 0.01 to 4MW, and the voltage is 380V.
Induction heating uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to increase the temperature of metal objects affected by a changing magnetic field. It converts electrical energy into electromagnetic energy and then into heat energy, which is a fast heating method, but given that it uses electromagnetic induction heating, it is limited by the small power load of a single boiler and the lack of technical maturity, so its development is slow and its market share is not high. Due to the rapid development of electrode boilers, they are far superior to resistance and electromagnetic boilers in terms of operation and maintenance, high efficiency, control accuracy, start-stop speed, etc. These two types of boilers are gradually being replaced.
The EPCB boiler is a comparative study of the differences in the design of submerged and injected electrode boilers and resistance boiler rooms.
Electric Boiler Room Design
Unlike gas-fired boilers, electric boiler houses do not require a flue gas system, nor do they require a fuel supply and flue gas system like coal-fired or biomass-fired boiler houses, and they do not require dust removal, desulfurization, and denitrification devices to meet local environmental requirements for boiler emissions.

1 Submerged and injected electrode boiler room design
Electrode boilers are divided into immersion type and injection type according to the different ways of contact between water flow and electrodes. Since the power load of these two types of electrode boilers is the same for a single boiler, when designing and selecting a boiler for a boiler room, the differences in operation and design should be evaluated in detail, and the equipment with more mature technology and easier and safer operation and maintenance should be selected.
The electrode type electric heating boiler in which the electrodes are fully or partially submerged in the electrode mass is the submerged electrode boiler; the electrode type electric heating boiler in which the electrode mass is sprayed between the electrodes and the electrode medium is used to connect the electrodes so as to form a current circuit is called the spray electrode boiler.
Both boilers use water as a resistance for heating, and water as a conductor, so the conductivity of the water is controlled within a specific range is necessary. If the conductivity is too low, the boiler will not reach its rated output; if the conductivity is too high, it will cause a short circuit and an accident. But the biggest difference between the two is that the gap between them and the water is different. the boiler requires different conductivity of the water.
As the submerged electrode boiler, the electrode rod is submerged in water, the contact resistance with water is small and the conductivity is large, so this boiler needs to control the conductivity within a reasonable range, otherwise, it will cause electric breakdown accidents. The furnace water conductivity needs to be controlled at ≤ 200us/cm, so the boiler body make-up water must use demineralized water. While the spray electrode boiler has a large contact gap with the water, the conductivity of the furnace water needs to be controlled at > 2000us/cm, the boiler body make-up water using softened water can meet the requirements.
In the design of submerged electrode boiler room, in addition to the conventional water softener, make-up water tank and make-up water pump, additional equipment such as desalination device is required to reduce the content of electrolyte in the feed water, and when the conductivity of circulating water reaches 200μs/cm, the boiler inner tube is drained to discharge the high conductivity furnace water and reduce the conductivity of furnace water in the inner tube to within the normal limit. The conductivity of the boiler water in the inner tube of the boiler is reduced to within the normal limit.
In addition to the difference in water replenishment, the two boilers also differ in the body circulation water volume, now both boilers with electric power of 8MW (rated evaporation capacity of 12t/h), for example, the submerged electrode boiler takes into account the amount of primary evaporation of pot water and facilitates the mixing of water temperature in the furnace, the body circulation water volume is 21.6m3 /h and the power is 5.5kW; while the jet electrode boiler requires high electrical conductivity and needs to increase the furnace water flow rate to avoid the evaporation in the furnace cannot be carried away effectively.
The boiler body circulation water volume is 450m3/h and the power is 30KW; the boiler body circulation pump needs to run 24h and the average daily power consumption of single boiler body circulation pump is 588kWh, so the operating cost of the body circulation pump of the jet electrode boiler is much higher than that of the submerged electrode boiler. The end heating circulation system is no different from the conventional system in terms of setup and equipment selection, so we will not repeat here.
As mentioned above, the performance of the two boilers differs somewhat due to the difference in their structural forms. Jet electrode boilers require high conductivity of furnace water, which is prone to arc pulling, high concentration of sodium ions in steam, and difficulties in controlling jet water flow, while submerged boilers operate with low conductivity, good internal arc extinguishing, high three-phase balance, and good steam quality, and the hydrogen gas explosion accident that occurred in 1983 at the start-up boiler maintenance of a Swiss nuclear power plant directly led to the ban of these boilers in Europe. The use of such boilers was banned in Europe and is now only used in the United States and Canada, so submerged electrode boilers have gradually become the mainstream development and application trend of electric boilers.
2 Boiler room design for resistance boilers
The resistance boiler converts electrical energy into heat energy through electrical resistance and then transfers it to water. Water is only used as the heat transfer medium and not as the resistance, and the heating medium is water, so the resistance boiler only needs to be set up according to the conventional heating cycle system, and no additional auxiliary equipment is needed, so we will not elaborate on it here.
3 Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of resistance and electrode boilers
From the perspective of reliability and safety, the conventional resistance boiler is a standard product and uses a low-voltage power supply system, which is safer than the high-voltage electrode boiler.
In terms of heating performance, the two boilers have different heating principles, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In terms of control and operation, the conventional low-voltage resistance boiler uses a set of conventional components and is simpler and easier to control than the electrode boiler.
In terms of investment, resistance boilers require voltage distribution equipment, while electrode boilers require additional auxiliary heat exchange equipment, and the difference between the initial investment of the two boilers is not significant. From the perspective of land occupation, as the resistance boiler needs to be equipped with transformers and other low-voltage equipment, its land occupation is much larger than that of the electrode boiler.
From the operation and maintenance point of view, electrode boilers have more auxiliary equipment and resistance boilers have more electrical equipment, which require a certain amount of operation and maintenance. From the perspective of load regulation, the electrode boiler is adjustable within 1% to 100% of the load range, and the load curve is smooth and the load change can be adjusted infinitely;
The resistance boiler is adjustable within 20% to 100% of the load range, and the load curve is stepped because it relies on the number of resistance rods to adjust the load change. From the point of view of operation and maintenance safety, resistance boilers are prone to water shortage and dry burning, which is easy to burn out; electrode boilers are short of water, that is, the electrical system breaks down, which does not cause dry burning accidents and is safer. From the perspective of start-up speed, resistance boilers can reach full load in 10 to 20 minutes;
Electrode boilers can reach full load from cold standby in 5 minutes. In summary, resistance boilers and electrode boilers have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of performance and economy, and the selection of boiler equipment suitable for the design project can be considered from the perspective of the initial investment, the number of boilers selected, the capacity of individual boilers, and the technical ability of project operation and maintenance personnel.
4 Electrode boiler and resistance boiler equipment selection
As the core equipment in the boiler room heating system, before designing the boiler room, it is necessary to have a full understanding of the performance of the different boiler bodies selected in order to reasonably configure the auxiliary heating equipment and design a more reasonable heating system. In the process of boiler equipment selection, the performance of the equipment needs to be considered comprehensively, but more importantly, the safety is considered.
From the perspective of single equipment thermal power, when the power load of single boiler is above 4MW, electrode boiler is considered after comprehensive economic analysis; when the power load of single boiler is below 4MW, resistance boiler is considered as the heat source of boiler room, because from the perspective of heating load regulation, it is not recommended that the boiler body works in low load area for a long time, and resistance boiler is more suitable for small heating heat load.
The reason is that from the perspective of heating load regulation, it is not recommended to work the boiler body in the low load area for a long time, and the choice of resistance boiler is more suitable for the heat load of small area heating; and from the perspective of control and operation performance, resistance boiler is a conventional control requirement, which is simple to learn, and the ordinary stoker can meet the operation and maintenance requirements, while the electrode boiler is mostly introduced from abroad and requires professional or strictly trained professional operators. The advantages of choosing resistance boilers over electrode boilers are greater.
Conclusion
This paper firstly introduces the development of electric boiler, its application and working principle, and then describes in detail the working principle and design control points of three popular electric boilers in China, which leads to the focus of this paper is to analyze and study the difference and application range of three typical electric boilers in boiler room design.
When the single electric power is above 4MW, electrode boiler is used, and when the single electric power is below 4MW, resistance boiler is used. With the increasing area of urban heating in China, the situation of energy saving and emission reduction is getting more and more serious, and the supply of natural gas is tight, electric energy, as a clean energy source, has its own unique advantages because of its small energy transmission restrictions. If the combined heating method of electric boiler and heat storage is adopted, it can balance the load of the power grid if it can make full use of the valley electricity as central heating, store heat in the low valley electricity and use heat in the high electricity price range.
This will be more in line with the general policy of energy saving and consumption reduction in China and widen the market space. At present, electrode boilers are still a new type of equipment in China, and their popularity in the market is not very high. However, in view of the advantages of electric boilers, such as small footprint, fast start/stop , high control accuracy, easy operation and maintenance, high efficiency and energy saving, green environment, etc., they have become the focus of attention and research of scholars in the industry, and the research results on electric boilers are also quite rich. Based on this paper, several typical types of electric boilers are analyzed and compared, in order to provide some design ideas for practitioners of boiler room design, and the choice of boilers can be further analyzed and determined according to specific projects.
 Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Thermal Oil Boiler
Thermal Oil Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler Steam Boiler
Steam Boiler Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boiler